Geography Available Research Project
Debris flow erosion and sediment transport in the Cairngorms, Scottish Highlands
Debris flows are key drivers of erosion and sediment transport in mountainous areas and are significant hazards to both human populations and infrastructure. Sediment supply from debris flows has important implications for downstream flood risk and channel migration. However, our ability to quantify debris flow hazard is limited by our poor understanding of where they occur. This is a major issue for quantifying hazard and making reasonable estimates of debris flow risk.
The steep, mountainous regions of the Scottish Highlands are commonly affected by debris flows. However, little work has been done in quantifying the extent of debris flows in the region or assessing whether these processes contribute to shaping the modern landscape. The extent to which debris flows erode and deliver sediment to downstream river channels is an open question. This project will explore debris flow gullies in the Cairngorms, Scottish Highlands, using a combination of field work, high-resolution laser scanning, and topographic analysis. The aim of the project is to map the extent and characteristics (length, width, grain size) of debris flow gullies along Glen Feshie. These will constrain a sediment budget for this steep, mountainous catchment to quantify the contribution of debris flows to downstream sediment transport. The key research questions of this project are:
- Where do debris flows occur in the landscape?
- Do debris flows erode material and contribute to modern sediment loads in the Cairngorms?
- How is sediment generated from debris flow events moved through catchments?
Project Inquiries & Applications
For more information about this project or to discuss your research ideas contact Lead supervisor(s): Dr. Fiona Clubb and Dr. Elizabeth Dingle

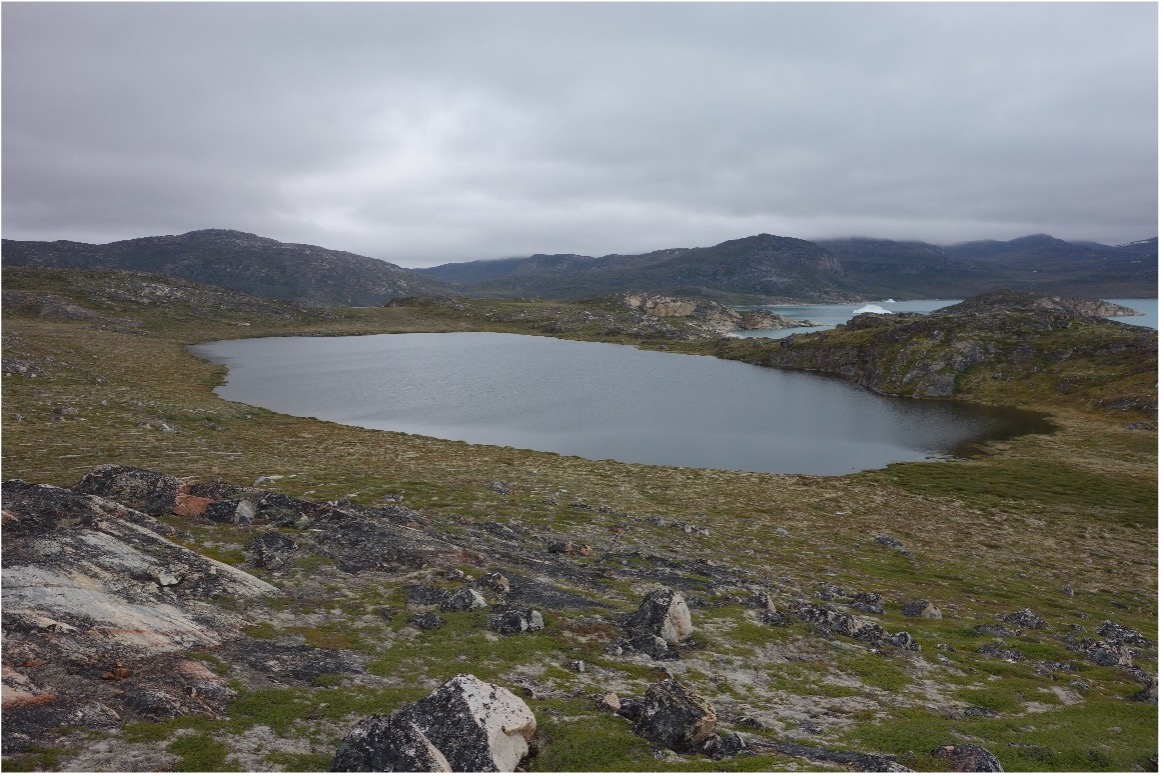
Debris flows supplying sediment to the River Feshie, Caingorms, Scotland
Key references:
Stock, J. and Dietrich, W.E., 2003. Valley incision by debris flows: Evidence of a topographic signature. Water Resources Research, 39(4).
McCoy, S.W., Kean, J.W., Coe, J.A., Staley, D.M., Wasklewicz, T.A. and Tucker, G.E., 2010. Evolution of a natural debris flow: In situ measurements of flow dynamics, video imagery, and terrestrial laser scanning. Geology, 38(8), pp.735-738.
Mueting, A., Bookhagen, B. and Strecker, M.R., 2021. Identification of Debris‐Flow Channels Using High‐Resolution Topographic Data: A Case Study in the Quebrada del Toro, NW Argentina. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 126(12), p.e2021JF006330.
Available Research Projects
See all of the currently available research projects that are recruiting students.
Research Masters
Our Research Masters provides an opportunity to develop your research expertise and advanced skills. Pursue your own top or collaborate on a project designed by a supervisor in our world-leading research environment.
Contact Us
Founded in 1928, the Department of Geography at Durham University is one of the leading centres of geographical research and education in the world.
Department of Geography
Postgraduate Study
Durham University
Lower Mountjoy
South Road, Durham
DH1 3LE, UK
Tel: +44 (0)191 33418000


/prod01/prodbucket01/media/durham-university/departments-/geography/Matt_Couchmann-3872X1296.JPG)