Staff profile
Dr Gary Sharples
Associate Professor

| Affiliation | Telephone |
|---|---|
| Associate Professor in the Department of Biosciences | +44 (0) 191 33 43986 |
Biography
I am interested in the mode of action of more unorthodox antimicrobial agents. I studied microbiology at Glasgow University, followed by a PhD in bacterial genetics at the University of Nottingham. There I studied the molecular mechanisms of bacterial and bacteriophage genome rearrangements, with a focus on DNA structure-specific endonucleases and helicases. Since moving to Durham in 2001, and relocation to the Chemistry Department here, I have become increasingly interested in antimicrobials. Work with chemists has included analysis of novel antimicrobial surfaces, polymers, nanoparticles, peptoids, therapeutic clays and other small molecules. Current major projects involve collaboration with industry, namely metal chelating agents with Procter & Gamble and photoactivatable antimicrobials with LightOx Ltd. A major goal is to identify alternatives for our dwindling supply of antibiotics to combat drug resistant bacteria and fungi.
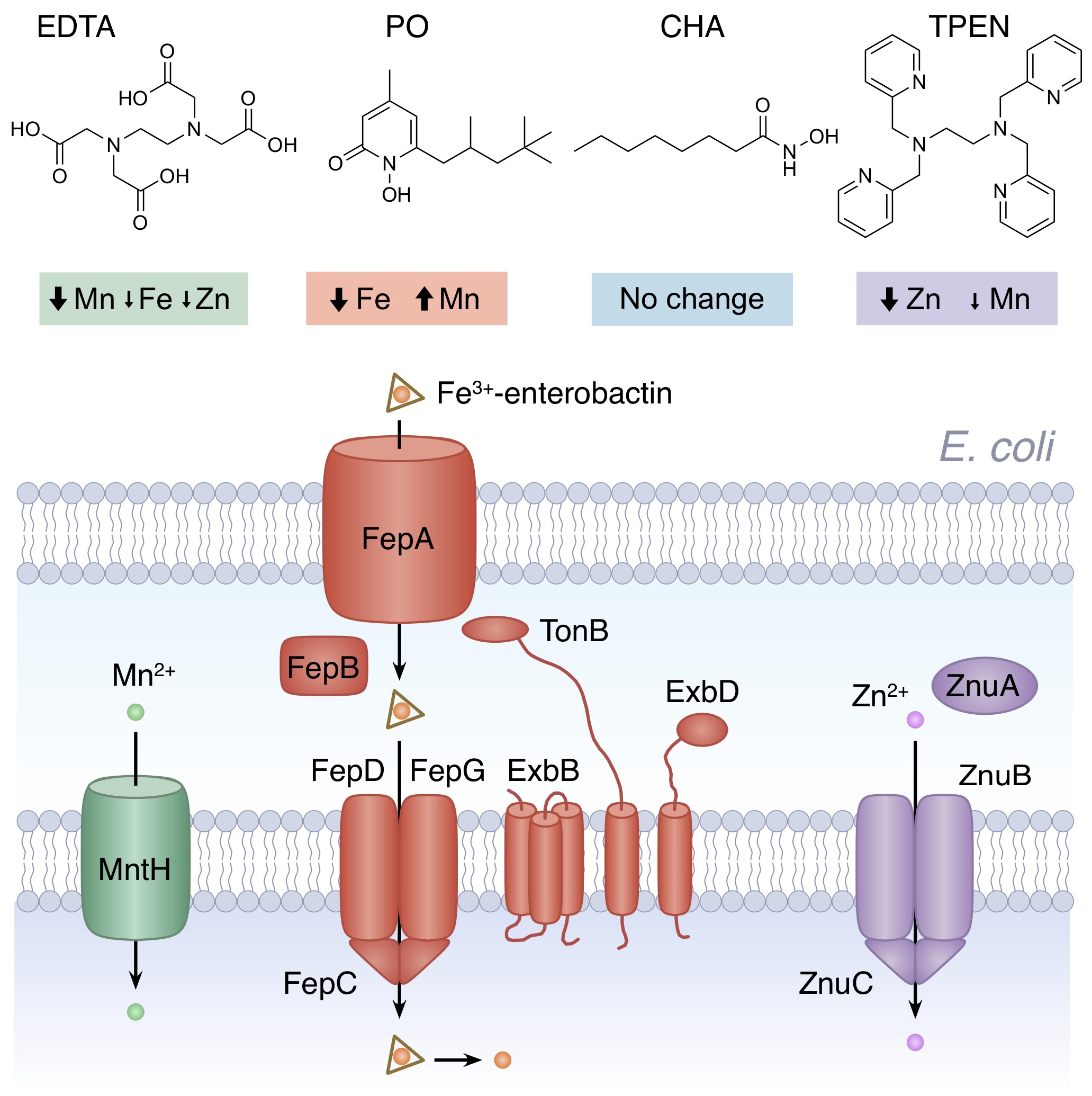
Metal chelating agents target different metals in bacteria. The four examples shown above highlight some of the metals affected in Escherichia coli and the uptake pathways important for tolerance. Further details can be found in Paterson et al (2022) listed below.
Research interests
- Microbiology
- Bacterial and bacteriophage genome rearrangements
- Antibacterial agents and resistance mechanisms
- Novel antimicrobial surfaces
- Metals in microbiology
- Photoactivatable antimicrobials
Esteem Indicators
- 1992 - 2000: Royal Society University Research Fellowship: 1992-2000:
Publications
Chapter in book
- The RuvAB and RecG proteins of Escherichia coli.Whitby, M., Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (1995). The RuvAB and RecG proteins of Escherichia coli. In F. E. Eckstein (Ed.), Nucleic Acids and Molecular Biology (pp. 66-83). Springer Verlag. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-79488-9_4
Journal Article
- Antibacterial chelating agents with applications in industry and medicine: cellular metal restriction, membrane disruption and synergism with antibiotics in Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens, Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus.Paterson, J. R., Hardman, B. L., Jordan, L. A., Wadsworth, J. M., Black, D. J., Ross, J., Clare, L. A., Wright, E., Wallace, E. R., Pal, R., Moran, M. T., & Sharples, G. J. (2025). Antibacterial chelating agents with applications in industry and medicine: cellular metal restriction, membrane disruption and synergism with antibiotics in Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens, Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 136(11), Article lxaf258. https://doi.org/10.1093/jambio/lxaf258
- Anti-biofilm mechanism of Malaysian natural clay against food-borne Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella TyphimuriumWan Omar, W. H., Mahyudin, N. A., Azmi, N. N., Mahmud Ab Rashid, N., Ismail, R., & Sharples, G. J. (2025). Anti-biofilm mechanism of Malaysian natural clay against food-borne Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella Typhimurium. The Microbe, 7, Article 100403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microb.2025.100403
- Enhanced resistance of metal sequestering agents by reconfiguration of the Staphylococcus aureus cell wallPaterson, J. R., Wadsworth, J. M., Lee, R. J., Hu, P., Biboy, J., Vollmer, D., Vollmer, W., Marles-Wright, J., Radin, J. N., Kehl-Fie, T. E., Moran, M. T., & Sharples, G. J. (2025). Enhanced resistance of metal sequestering agents by reconfiguration of the Staphylococcus aureus cell wall. Npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, 3, Article 61. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44259-025-00131-1
- Evaluation of the antibacterial properties of commonly used clays from deposits in central and southern AsiaAbdullayev, E., Paterson, J. R., Kuszynski, E. P., Hamidi, M. D., Nahar, P., Greenwell, H. C., Neumann, A., & Sharples, G. J. (2024). Evaluation of the antibacterial properties of commonly used clays from deposits in central and southern Asia. Clays and Clay Minerals, 72, Article e9. https://doi.org/10.1017/cmn.2024.7
- Antibacterial mechanism of Malaysian Carey clay against food-borne Staphylococcus aureusAzmi, N. N., Mahyudin, N. A., Wan Omar, W. H., Abdullah, A. H., Ismail, R., Ishak, C. F., & Sharples, G. J. (2024). Antibacterial mechanism of Malaysian Carey clay against food-borne Staphylococcus aureus. Natural Product Research. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2024.2355583
- A critical role for iron and zinc homeostatic systems in the evolutionary adaptation of Escherichia coli to metal restrictionPaterson, J. R., Wadsworth, J. M., Hu, P., & Sharples, G. J. (2023). A critical role for iron and zinc homeostatic systems in the evolutionary adaptation of Escherichia coli to metal restriction. Microbial Genomics, 9(12), Article 001153. https://doi.org/10.1099/mgen.0.001153
- Effect of natural antibacterial clays against single biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella Typhimurium bacteria on a stainless-steel surfaceWan Omar, W. H., Mahyudin, N. A., Azmi, N. N., Mahmud Ab Rashid, N., Ismail, R., Mohd Yusoff, M. H. Y., Khairil Mokhtar, N. F., & Sharples, G. J. (2023). Effect of natural antibacterial clays against single biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella Typhimurium bacteria on a stainless-steel surface. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 394, Article 110184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2023.110184
- Reading Clay: The Temporal and Transformative Potential of Clay in Contemporary Scientific PracticeBryant, L., Jamie, K., & Sharples, G. (2023). Reading Clay: The Temporal and Transformative Potential of Clay in Contemporary Scientific Practice. Journal of Material Culture, 28(1), 87-105. https://doi.org/10.1177/13591835221074159
- The antibacterial activity of a photoactivatable diarylacetylene against Gram-positive bacteriaWaite, R., Adams, C. T., Chisholm, D. R., Sims, C. H. C., Hughes, J. G., Dias, E., White, E. A., Welsby, K., Botchway, S. W., Whiting, A., Sharples, G. J., & Ambler, C. A. (2023). The antibacterial activity of a photoactivatable diarylacetylene against Gram-positive bacteria. Frontiers in Microbiology, 14, Article 1243818. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1243818
- Nature‐Inspired Substrate‐Independent Omniphobic and Antimicrobial Slippery SurfacesCox, H. J., Gibson, C. P., Sharples, G. J., & Badyal, J. P. S. (2022). Nature‐Inspired Substrate‐Independent Omniphobic and Antimicrobial Slippery Surfaces. Advanced Engineering Materials, 24(6), Article 2101288. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.202101288
- Insights into the antibacterial mechanism of action of chelating agents by selective deprivation of iron, manganese and zincPaterson, J. R., Beecroft, M. S., Mulla, R. S., Osman, D., Reeder, N. L., Caserta, J. A., Young, T. R., Pettigrew, C. A., Davies, G. E., Williams, J. G., & Sharples, G. J. (2022). Insights into the antibacterial mechanism of action of chelating agents by selective deprivation of iron, manganese and zinc. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 88(2), Article e01641-21. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01641-21
- Antibacterial Activity of Clay Soils against Food-Borne Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureusAzmi, N. N., Mahyudin, N. A., Wan Omar, W. H., Mahmud Ab Rashid, N., Ishak, C. F., Abdullah, A. H., & Sharples, G. J. (2022). Antibacterial Activity of Clay Soils against Food-Borne Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules, 27(1), Article 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010170
- Tea–Essential Oil–Metal Hybrid Nanocoatings for Bacterial and Viral InactivationCox, H. J., Sharples, G. J., & Badyal, J. P. S. (2021). Tea–Essential Oil–Metal Hybrid Nanocoatings for Bacterial and Viral Inactivation. ACS Applied Nano Materials., 4(11), 12619-12628. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c03151
- Bioinspired and eco-friendly high efficacy cinnamaldehyde antibacterial surfacesCox, H. J., Li, J., Saini, P., Paterson, J. R., Sharples, G. J., & Badyal, J. P. S. (2021). Bioinspired and eco-friendly high efficacy cinnamaldehyde antibacterial surfaces. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 9(12), 2918-2930. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0tb02379e
- Volcanism and global plague pandemics: Towards an interdisciplinary synthesisFell, H. G., Baldini, J. U., Dodds, B., & Sharples, G. J. (2020). Volcanism and global plague pandemics: Towards an interdisciplinary synthesis. Journal of Historical Geography, 70, 36-46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhg.2020.10.001
- A bacteriophage mimic of the bacterial nucleoid-associated protein FisSharples, G. J., Heddle, J. G., Kozak, M., Taube, M., Hughes, T. R., Pålsson, L., Bowers, L. Y., Curtis, F. A., Plewka, J., Świątek, S., Paterson, J. R., Jolma, A., Yang, A. W. H., Gittens, W. H., Trotter, A. J., Balakrishnan, D., & Chakraborti, S. (2020). A bacteriophage mimic of the bacterial nucleoid-associated protein Fis. Biochemical Journal, 477(7), 1345-1362. https://doi.org/10.1042/bcj20200146
- The social and material life of medicinal clay: Exploring antimicrobial resistance, medicines' materiality and medicines optimizationJamie, K., & Sharples, G. (2020). The social and material life of medicinal clay: Exploring antimicrobial resistance, medicines’ materiality and medicines optimization. Frontiers in Sociology, 5, Article 26. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsoc.2020.00026
- Bioinspired Multifunctional Polymer–Nanoparticle–Surfactant Complex Nanocomposite Surfaces for Antibacterial Oil–Water SeparationRitchie, A., Cox, H., Barrientos-Palomo, S., Sharples, G., & Badyal, J. (2019). Bioinspired Multifunctional Polymer–Nanoparticle–Surfactant Complex Nanocomposite Surfaces for Antibacterial Oil–Water Separation. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 560, 352-359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.10.030
- On the antibacterial activity of azacarboxylate ligands: lowered metal ion affinities for bis-amide derivatives of EDTA do not mean reduced activityMulla, R. S., Beecroft, M. S., Pal, R., Aguilar, J., Pitarch-Jarque, J., García‐España, E., Lurie-Luke, E., Sharples, G., & Williams, J. (2018). On the antibacterial activity of azacarboxylate ligands: lowered metal ion affinities for bis-amide derivatives of EDTA do not mean reduced activity. Chemistry - A European Journal, 24(28), 7137-7148. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201800026
- The intracellular immune receptor Rx1 regulates the DNA-binding activity of a Golden2-like transcription factorTownsend, P., Dixon, C., Slootweg, E., Sukarta, O., Yang, A., Hughes, T., Sharples, G., Palsson, L., Takken, F., Goverse, A., & Cann, M. (2018). The intracellular immune receptor Rx1 regulates the DNA-binding activity of a Golden2-like transcription factor. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 293(9), 3218-3233. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.ra117.000485
- Medicinal Mascarene Aloe s: An audit of their phytotherapeutic potentialLobine, D., Cummins, I., Govinden-Soulange, J., Ranghoo-Sanmukhiya, M., Lindsey, K., Chazot, P., Ambler, C., Grellscheid, S., Sharples, G., Lall, N., Lambrechts, I., Lavergne, C., & Howes, M. (2018). Medicinal Mascarene Aloe s: An audit of their phytotherapeutic potential. Fitoterapia, 124, 120-126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2017.10.010
- Exploring the links between peptoid antibacterial activity and toxicityBolt, H. L., Eggimann, G. A., Jahoda, C. A., Zuckermann, R. N., Sharples, G. J., & Cobb, S. L. (2017). Exploring the links between peptoid antibacterial activity and toxicity. MedChemComm., 8(5), 886-896. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6md00648e
- Glycosylated nanoparticles as efficient antimicrobial delivery agentsEissa, A., Abdulkarim, A., Sharples, G., & Cameron, N. (2016). Glycosylated nanoparticles as efficient antimicrobial delivery agents. Biomacromolecules, 17(8), 2672-2679. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.6b00711
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis RuvX is a Holliday junction resolvase formed by dimerisation of the monomeric YqgF nuclease domainNautiyal, A., Rani, P., Sharples, G., & Muniyappa, K. (2016). Mycobacterium tuberculosis RuvX is a Holliday junction resolvase formed by dimerisation of the monomeric YqgF nuclease domain. Molecular Microbiology, 100(4), 656-674. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.13338
- The tomato Nucleotide-Binding Leucine-Rich Repeat (NLR) Immune Receptor I-2 couples DNA-Binding to Nucleotide-Binding Domain Nucleotide ExchangeFenyk, S., Dixon, C. H., Kittens, W. H., Townsend, P. D., Sharples, G. .J., Pålsson, L. O., Takken, F. L. W., & Cann, M. J. (2016). The tomato Nucleotide-Binding Leucine-Rich Repeat (NLR) Immune Receptor I-2 couples DNA-Binding to Nucleotide-Binding Domain Nucleotide Exchange. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 291(3), 1137-1147. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m115.698589
- Preparation of an antibacterial poly(ionic liquid) graft copolymer of hydroxyethyl celluloseJoubert, F., Yeo, R. P., Sharples, G. J., Musa, O. M., Hodgson, D. R., & Cameron, N. R. (2015). Preparation of an antibacterial poly(ionic liquid) graft copolymer of hydroxyethyl cellulose. Biomacromolecules, 16(12), 397-3979. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.5b01300
- The Potato Nucleotide-Binding Leucine-Rich Repeat (NLR) Immune Receptor Rx1 is a Pathogen Dependent DNA-Deforming ProteinFenyk, S., Townsend, P. D., Dixon, C. H., Spies, G. B., de San Eustaquio Campillo, A., Slootweg, E. J., Westerhof, L. B., Gawehns, F. K., Knight, M. R., Sharples, G. J., Goverse, A., Pålsson, L., Takken, F. L., & Cann, M. J. (2015). The Potato Nucleotide-Binding Leucine-Rich Repeat (NLR) Immune Receptor Rx1 is a Pathogen Dependent DNA-Deforming Protein. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 290(41), 24945-24960. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m115.672121
- Preparation, properties, and antibacterial behavior of a novel cellulose derivative containing lactam groupsJoubert, F., Sharples, G. J., Musa, O. M., Hodgson, D. R., & Cameron, N. R. (2015). Preparation, properties, and antibacterial behavior of a novel cellulose derivative containing lactam groups. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 53(1), 68-78. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.27441
- Phage Orf family recombinases: conservation of activities and involvement of the central channel in DNA bindingCurtis, F., Malay, A., Trotter, A., Wilson, L., Barradell-Black, M., Bowers, L., Reed, P., Hillyar, C., Yeo, R., Sanderson, J., Heddle, J., & Sharples, G. (2014). Phage Orf family recombinases: conservation of activities and involvement of the central channel in DNA binding. PLoS ONE, 9(8), Article e102454. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0102454
- Structural and functional characterization of the Redβ recombinase from bacteriophage λMatsubara, K., Malay, A., Curtis, F., Sharples, G., & Heddle, J. (2013). Structural and functional characterization of the Redβ recombinase from bacteriophage λ. PLoS ONE, 8(11), Article e78869. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0078869
- Mutants of phage bIL67 RuvC with enhanced Holliday junction binding selectivity and resolution symmetryGreen, V., Curtis, F., Sedelnikova, S., Rafferty, J., & Sharples, G. (2013). Mutants of phage bIL67 RuvC with enhanced Holliday junction binding selectivity and resolution symmetry. Molecular Microbiology, 89(6), 1240-1258. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.12343
- Electroless deposition of multi-functional zinc oxide surfaces displaying photoconductive, superhydrophobic, photowetting, and antibacterial propertiesWood, T., Hurst, G., Schofield, W., Thompson, R., Oswald, G., Evans, J., Sharples, G., Pearson, C., Petty, M., & Badyal, J. (2012). Electroless deposition of multi-functional zinc oxide surfaces displaying photoconductive, superhydrophobic, photowetting, and antibacterial properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 22(9), 3859-3867. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm14260k
- The C-terminus of the phage λ Orf recombinase is involved in DNA bindingCurtis, F. A., Reed, P., Wilson, L. A., Bowers, L. Y., Yeo, R. P., Sanderson, J. M., Walmsley, A. R., & Sharples, G. J. (2011). The C-terminus of the phage λ Orf recombinase is involved in DNA binding. Journal of Molecular Recognition, 24(2), 333-340. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmr.1079
- The N-terminal region of the RecU Holliday junction resolvase is essential for homologous recombination.Carrasco, B., Cañas, C., Sharples, G., Alonso, J., & Ayora, S. (2009). The N-terminal region of the RecU Holliday junction resolvase is essential for homologous recombination. Journal of Molecular Biology, 390(1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2009.04.065
- For absent friends: life without recombination in mutualistic gamma-proteobacteriaSharples, G. (2009). For absent friends: life without recombination in mutualistic gamma-proteobacteria. Trends in Microbiology, 17(6), 233-242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2009.03.005
- Novel antibiotics: C-2 symmetrical macrocycles inhibiting Holliday junction DNA binding by E. coli RuvC.Pan, P., Curtis, F., Carroll, C., Medina, I., Rodrigeuz, R., Liotta, L., Sharples, G., & McAlpine, S. (2006). Novel antibiotics: C-2 symmetrical macrocycles inhibiting Holliday junction DNA binding by E. coli RuvC. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 14(14), 4731-4739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2006.03.028
- Functional similarities between phage lambda Orf and Escherichia coli RecFOR in initiation of genetic exchangeMaxwell, K., Reed, P., Zhang, R., Beasley, S., Walmsley, A., Curtis, F., Joachimiak, A., Edwards, A., & Sharples, G. (2005). Functional similarities between phage lambda Orf and Escherichia coli RecFOR in initiation of genetic exchange. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 102(32), 11260-11265. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0503399102
- Evolution of a phage RuvC endonuclease for resolution of both Holliday and branched DNA junctionsCurtis, F., Reed, P., & Sharples, G. (2005). Evolution of a phage RuvC endonuclease for resolution of both Holliday and branched DNA junctions. Molecular Microbiology, 55(5), 1332-1345. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04476.x
- Conservation of RecG activity from pathogens to hyperthermophiles.Wen, Q., Mahdi, A., Briggs, G., Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (2005). Conservation of RecG activity from pathogens to hyperthermophiles. DNA Repair, 4, 23-31.
- The RuvAB branch migration translocase and RecU Holliday junction resolvase are required for double-stranded DNA break repair in Bacillus subtilis.Sanchez, H., Kidane, D., Reed, P., Curtis, F., Cozar, M., Graumann, P., Sharples, G., & Alonso, J. (2005). The RuvAB branch migration translocase and RecU Holliday junction resolvase are required for double-stranded DNA break repair in Bacillus subtilis. Genetics, 171, 873-883.
- VceR regulates the vceCAB drug efflux pump operon of Vibrio cholerae by alternating between mutually exclusive conformations that bind either drugs or promoter DNA.Borges-Walmsley, M., Du, D., McKeegan, K., Sharples, G., & Walmsley, A. (2005). VceR regulates the vceCAB drug efflux pump operon of Vibrio cholerae by alternating between mutually exclusive conformations that bind either drugs or promoter DNA. Journal of Molecular Biology, 349(2), 387-400.
- Holliday Junction Binding and Resolution by the Rap Structure-specific Endonuclease of Phage lambdaSharples, G., Curtis, F., McGlynn, P., & Bolt, E. (2004). Holliday Junction Binding and Resolution by the Rap Structure-specific Endonuclease of Phage lambda. Journal of Molecular Biology, 340(4), 739-751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.030
- DNA binding by the meningococcal RdgC protein associated with pilin antigenic variationMoore, T., Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (2004). DNA binding by the meningococcal RdgC protein associated with pilin antigenic variation. Journal of Bacteriology, 186, 870-874.
- Novel antibiotics: second generation macrocyclic peptides designed to trap Holliday junctions.Liotta, L., Medina, I., Robinson, J., Carroll, C., Pan, P., Corral, R., Cook, K., Johnston, J., Curtis, F., Sharples, G., & McAlpine, S. (2004). Novel antibiotics: second generation macrocyclic peptides designed to trap Holliday junctions. Tetrahedron Letters, 45, 8447-8450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2004.09.084
- A model for dsDNA translocation revealed by a structural motif common to RecG and Mfd proteins.Mahdi, A., Briggs, G., Sharples, G., Wen, Q., & Lloyd, R. (2003). A model for dsDNA translocation revealed by a structural motif common to RecG and Mfd proteins. EMBO Journal, 22, 724-734.
- Helicobacter pylori mutants defective in RuvC Holliday junction resolvase display reduced macrophage survival and spontaneous clearance from the murine gastric mucosa.Loughlin, M., Barnard, F., Jenkins, D., Sharples, G., & Jenks, P. (2003). Helicobacter pylori mutants defective in RuvC Holliday junction resolvase display reduced macrophage survival and spontaneous clearance from the murine gastric mucosa. Infection and Immunity, 71, 2022-2031.
- The structure of Escherichia coli RusA endonuclease reveals a new Holliday junction DNA binding fold.Rafferty, J., Bolt, E., Muranova, T., Sedelnikova, S., Leonard, P., Pasquo, A., Baker, P., Rice, D., Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (2003). The structure of Escherichia coli RusA endonuclease reveals a new Holliday junction DNA binding fold. Structure, 11, 1557-1567.
- The RdgC protein of Escherichia coli binds DNA and counters a toxic effect of RecFOR in strains lacking the replication restart protein PriA.Moore, T., McGlynn, P., Ngo, H., Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (2003). The RdgC protein of Escherichia coli binds DNA and counters a toxic effect of RecFOR in strains lacking the replication restart protein PriA. EMBO Journal, 22, 735-745.
- RusA proteins from the extreme thermophile Aquifex aeolicus and lactococcal phage r1t resolve Holliday junctionsSharples, G., Bolt, E., & Lloyd, R. (2002). RusA proteins from the extreme thermophile Aquifex aeolicus and lactococcal phage r1t resolve Holliday junctions. Molecular Microbiology, 44(2), 549-559. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02916.x
- Holliday junction binding and processing by the RuvA protein of Mycoplasma pneumoniae.Ingleston, S., Dickman, M., Grasby, J., Hornby, D., Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (2002). Holliday junction binding and processing by the RuvA protein of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. European Journal of Biochemistry, 269, 1525-1533.
- The X philes: structure-specific endonucleases that resolve Holliday junctions.Sharples, G. (2001). The X philes: structure-specific endonucleases that resolve Holliday junctions. Molecular Microbiology, 39, 823-834. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02284.x
- Genetic analysis of an archaeal Holliday junction resolvase in Escherichia coli.Bolt, E., Lloyd, R., & Sharples, G. (2001). Genetic analysis of an archaeal Holliday junction resolvase in Escherichia coli. Journal of Molecular Biology, 310(3), 577-589.
- Analysis of conserved basic residues associated with DNA binding (Arg69) and catalysis (Lys76) by the RusA Holliday junction resolvase.Bolt, E., Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (2000). Analysis of conserved basic residues associated with DNA binding (Arg69) and catalysis (Lys76) by the RusA Holliday junction resolvase. Journal of Molecular Biology, 304, 165-176.
- The acidic pin of RuvA modulates Holliday junction binding and processing by the RuvABC resolvasome.Ingleston, S., Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (2000). The acidic pin of RuvA modulates Holliday junction binding and processing by the RuvABC resolvasome. EMBO Journal, 19, 6266-6274.
- Identification of three aspartic acid residues essential for catalysis by the RusA Holliday junction resolvase.Bolt, E., Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (1999). Identification of three aspartic acid residues essential for catalysis by the RusA Holliday junction resolvase. Journal of Molecular Biology, 286, 403-415.
- Holliday junction processing in bacteria: insights from the evolutionary conservation of RuvABC, RecG, and RusA.Sharples, G., Ingleston, S., & Lloyd, R. (1999). Holliday junction processing in bacteria: insights from the evolutionary conservation of RuvABC, RecG, and RusA. Journal of Bacteriology, 181, 5543-5550.
- DNA structure specificity of Rap endonuclease.Sharples, G., Corbett, L., McGlynn, P., & Bolt, E. (1999). DNA structure specificity of Rap endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Research, 27, 4121-4127.
- Structural similarities between Escherichia coli RuvA protein and other DNA-binding proteins and a mutational analysis of its binding to the Holliday junction.Rafferty, J., Ingleston, S., Hargreaves, D., Artymiuk, P., Sharples, G., Lloyd, R., & Rice, D. (1998). Structural similarities between Escherichia coli RuvA protein and other DNA-binding proteins and a mutational analysis of its binding to the Holliday junction. J. Mol. Biol, 278, 105-116.
- Lambda Rap protein is a structure-specific endonuclease involved in phage recombination.Sharples, G., Corbett, L., & Graham, I. (1998). Lambda Rap protein is a structure-specific endonuclease involved in phage recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 95, 13507-13512.
- Sequence-specificity of Holliday junction resolution: identification of RuvC mutants defective in metal binding and target site recognition.Hagan, N., Vincent, S., Ingleston, S., Sharples, G., Bennett, R., West, S., & Lloyd, R. (1998). Sequence-specificity of Holliday junction resolution: identification of RuvC mutants defective in metal binding and target site recognition. Journal of Molecular Biology, 281, 17-29.
- Characterization of a thermosensitive Escherichia coli aspartyl-tRNA synthetase mutant.Martin, F., Sharples, G., Lloyd, R., Eiler, S., Moras, D., Gangloff, J., & Eriani, G. (1997). Characterization of a thermosensitive Escherichia coli aspartyl-tRNA synthetase mutant. Journal of Bacteriology, 179(11), 3691-3696.
- Recombination is unaffected by mutation of E. coli mfd.Sharples, G., & Corbett, L. (1997). Recombination is unaffected by mutation of E. coli mfd. Microbiology, 143, 690-691.
- Recombination-dependent growth in exonuclease-depleted recBC sbcBC strains of Escherichia coli K-12.Ryder, L., Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (1996). Recombination-dependent growth in exonuclease-depleted recBC sbcBC strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics, 143(3), 1101-1114.
- The mmsA locus of Streptococcus pneumoniae encodes a RecG-like protein involved in DNA repair and in three-strand recombination.Martin, B., Sharples, G., Humbert, O., Lloyd, R., & Claverys, J. (1996). The mmsA locus of Streptococcus pneumoniae encodes a RecG-like protein involved in DNA repair and in three-strand recombination. Molecular Microbiology, 19(5), 1035-1045.
- Crystal structure of DNA recombination protein RuvA and a model for its binding to the Holliday junction.Rafferty, J., Sedelnikova, S., Hargreaves, D., Artymiuk, P., Baker, P., Sharples, G., Mahdi, A., Lloyd, R., & Rice, D. (1996). Crystal structure of DNA recombination protein RuvA and a model for its binding to the Holliday junction. Science, 274(5286), 415-421.
- Haemophilus virulence.Sharples, G. (1996). Haemophilus virulence. Microbiology, 142 ( Pt 4).
- Holliday junction resolvases encoded by homologous rusA genes in Escherichia coli K-12 and phage 82.Mahdi, A., Sharples, G., Mandal, T., & Lloyd, R. (1996). Holliday junction resolvases encoded by homologous rusA genes in Escherichia coli K-12 and phage 82. J. Mol. Biol, 257(3), 561-573.
- Structural and functional similarities between the SbcCD proteins of Escherichia coli and the RAD50 and MRE11 (RAD32) recombination and repair proteins of yeast.Sharples, G., & Leach, D. (1995). Structural and functional similarities between the SbcCD proteins of Escherichia coli and the RAD50 and MRE11 (RAD32) recombination and repair proteins of yeast. Molecular Microbiology, 17(6), 1215-1217.
- Cloning, overexpression, purification, and characterization of the Escherichia coli RuvC Holliday junction resolvase.Dunderdale, H., Sharples, G., Lloyd, R., & West, S. (1994). Cloning, overexpression, purification, and characterization of the Escherichia coli RuvC Holliday junction resolvase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269(7), 5187-5194.
- Processing of intermediates in recombination and DNA repair: identification of a new endonuclease that specifically cleaves Holliday junctions.Sharples, G., Chan, S., Mahdi, A., Whitby, M., & Lloyd, R. (1994). Processing of intermediates in recombination and DNA repair: identification of a new endonuclease that specifically cleaves Holliday junctions. EMBO Journal, 13(24), 6133-6142.
- A mutation in helicase motif III of E. coli RecG protein abolishes branch migration of Holliday junctions.Sharples, G., Whitby, M., Ryder, L., & Lloyd, R. (1994). A mutation in helicase motif III of E. coli RecG protein abolishes branch migration of Holliday junctions. Nucleic Acids Research, 22(3), 308-313.
- Processing of recombination intermediates by the RecG and RuvAB proteins of Escherichia coli.Lloyd, R., & Sharples, G. (1993). Processing of recombination intermediates by the RecG and RuvAB proteins of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Research, 21(8), 1719-1725.
- Resolution of Holliday intermediates in recombination and DNA repair: indirect suppression of ruvA, ruvB, and ruvC mutations.Mandal, T., Mahdi, A., Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (1993). Resolution of Holliday intermediates in recombination and DNA repair: indirect suppression of ruvA, ruvB, and ruvC mutations. Journal of Bacteriology, 175(14), 4325-4334.
- An E. coli RuvC mutant defective in cleavage of synthetic Holliday junctions.Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (1993). An E. coli RuvC mutant defective in cleavage of synthetic Holliday junctions. Nucleic Acids Research, 21(15), 3359-3364.
- Dissociation of synthetic Holliday junctions by E. coli RecG protein.Lloyd, R., & Sharples, G. (1993). Dissociation of synthetic Holliday junctions by E. coli RecG protein. EMBO Journal, 12(1), 17-22.
- Location of the Bacillus subtilis sbcD gene downstream of addAB, the analogues of E. coli recBC.Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (1993). Location of the Bacillus subtilis sbcD gene downstream of addAB, the analogues of E. coli recBC. Nucleic Acids Research, 21(8). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/21.8.2010
- Genetic analysis of recombination in prokaryotes.Lloyd, R., & Sharples, G. (1992). Genetic analysis of recombination in prokaryotes. Current Opinion in Genetics and Development, 2(5), 683-690.
- Formation and resolution of recombination intermediates by E. coli RecA and RuvC proteins.Dunderdale, H., Benson, F., Parsons, C., Sharples, G., Lloyd, R., & West, S. (1991). Formation and resolution of recombination intermediates by E. coli RecA and RuvC proteins. Nature, 354(6354), 506-510.
- Molecular organization and nucleotide sequence of the recG locus of Escherichia coli K-12.Lloyd, R., & Sharples, G. (1991). Molecular organization and nucleotide sequence of the recG locus of Escherichia coli K-12. Journal of Bacteriology, 173(21), 6837-6843.
- Resolution of Holliday junctions in vitro requires the Escherichia coli ruvC gene product.Connolly, B., Parsons, C., Benson, F., Dunderdale, H., Sharples, G., Lloyd, R., & West, S. (1991). Resolution of Holliday junctions in vitro requires the Escherichia coli ruvC gene product. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 88(14), 6063-6067.
- Location of a mutation in the aspartyl-tRNA synthetase gene of Escherichia coli K12.Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (1991). Location of a mutation in the aspartyl-tRNA synthetase gene of Escherichia coli K12. Mutation Research - Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 264(3), 93-96.
- Resolution of Holliday junctions in Escherichia coli: identification of the ruvC gene product as a 19-kilodalton protein.Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (1991). Resolution of Holliday junctions in Escherichia coli: identification of the ruvC gene product as a 19-kilodalton protein. Journal of Bacteriology, 173(23), 7711-7715.
- A novel repeated DNA sequence located in the intergenic regions of bacterial chromosomes.Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (1990). A novel repeated DNA sequence located in the intergenic regions of bacterial chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Research, 18(22), 6503-6508.
- Molecular and functional analysis of the ruv region of Escherichia coli K-12 reveals three genes involved in DNA repair and recombination.Sharples, G., Benson, F., Illing, G., & Lloyd, R. (1990). Molecular and functional analysis of the ruv region of Escherichia coli K-12 reveals three genes involved in DNA repair and recombination. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 221(2), 219-226.
- Nucleotide sequencing of the ruv region of Escherichia coli K-12 reveals a LexA regulated operon encoding two genes.Benson, F., Illing, G., Sharples, G., & Lloyd, R. (1988). Nucleotide sequencing of the ruv region of Escherichia coli K-12 reveals a LexA regulated operon encoding two genes. Nucleic Acids Research, 16(4), 1541-1549.

